- Home
-
Products
- > 1 Phase Insert Pull SSR - GSI
- > 1 Phase Flip Covers SSR - GSP-C [HOT! ]
- > 1 Phase Anti-Slip SSR - GSP
- > 1 Phase Totally Metal SSR - GSQ
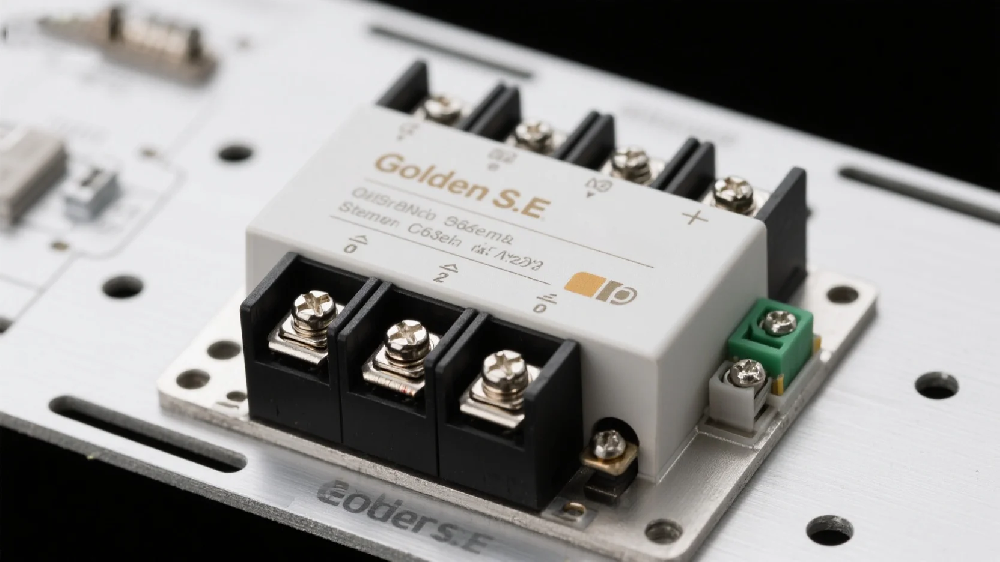
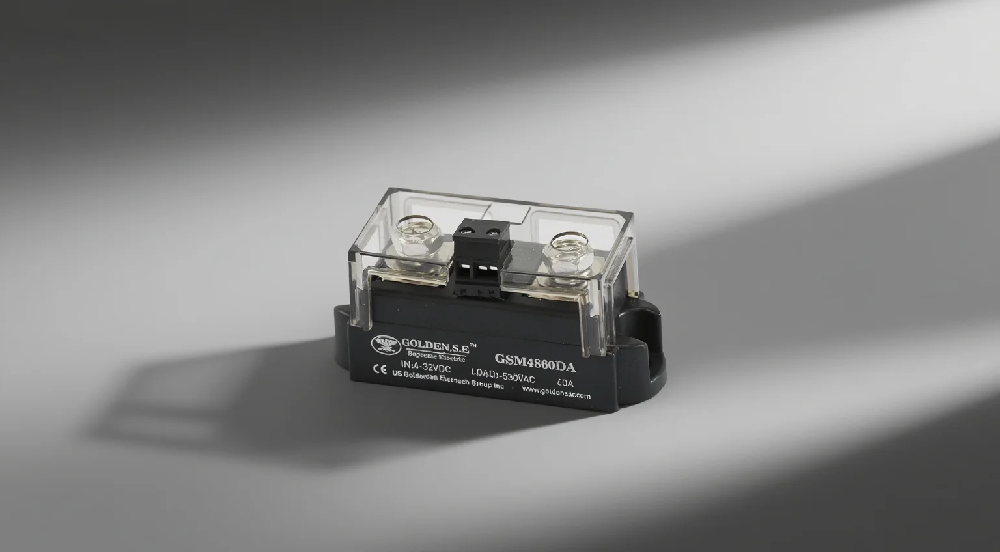
- > 1 Phase Modular SSR - GSM
- > 1 Phase Strip-Shape Flip Covers SSR - GST
- > 1 Phase Heatsink Integrated SSR - GSH [HOT! ]
- > 3 Phase Flip Covers SSR - GS3 [HOT! ]
- > 3 Phase Heatsink Integrated SSR - GS3H
- > Heatsink & Accessories
-
Industries
- > New energy & solar power
- > Air Conditioning & regulator equipment
-
> Traditional industries
- Glass Tempering Furnace
- Sintering Furnace
- Ceramic Sintering Furnace
- Chemical Fiber Equipment
- Elastic Yarn Machine
- Non-woven Mask Machine
- Bag Making Machine
- Textile Printing & Dyeing Machinery
- Printing Equipment
- Packaging Equipment
- Wire Drawing Machine
- Stamping Equipment
- Industrial Electric Furnace
- Fuel Dispenser Equipment
- Mining Machinery Equipment
- Automotive Production Equipment
- Heavy-duty Vehicles
- Glass Tempering Furnace
- > Plastic machinery industry
- > Food processing & medical equipment
- > Automated, semi & intelligent industry
- > Smart Home Systems
- > Smart Warehouse
- > Intelligent Solid-state Switchgear
- About Us
- Download
- Technology
- News
-
Contact Us
-
- > 1 Phase Insert Pull SSR - GSI
- > 1 Phase Flip Covers SSR - GSP-C [HOT! ]
- > 1 Phase Anti-Slip SSR - GSP
- > 1 Phase Totally Metal SSR - GSQ
- > 1 Phase Modular SSR - GSM
- > 1 Phase Strip-Shape Flip Covers SSR - GST
- > 1 Phase Heatsink Integrated SSR - GSH [HOT! ]
- > 3 Phase Flip Covers SSR - GS3 [HOT! ]
- > 3 Phase Heatsink Integrated SSR - GS3H
- > Heatsink & Accessories
-
+1 227 241 2073
goldenssr@goldenssr.com